In Q3 2022, researchers at Cisco Talos Incident Response (CTIR) released their quarterly report on incident response trends. Trends in ransomware, phishing, and BEC are among the key findings.
Key Takeaways from Incident Response Trends in Q3 2022
The Quarterly Report: Incident Response Trends in Q3 2022 was released by CTIR researchers on October 25, 2022. Major conclusions include:
Compared to last quarter, when commodities trojans narrowly outranked ransomware, ransomware emerged as the leading threat this quarter.
This quarter, CTIR interactions involved a number of prominent ransomware groups, including Vice Society and Hive.
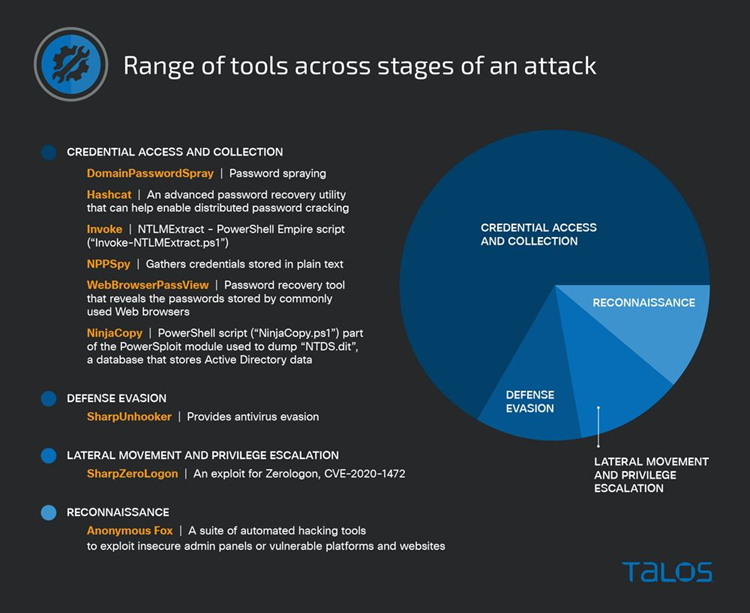
To enable operations at various phases of the attack lifecycle, CTIR saw adversaries using a number of publicly accessible tools. And scripts that were posted on GitHub repositories or via third-party websites.
Information thieves like Redline and common malware like the banking trojan Qakbot were the next most frequently spotted threats this quarter.

Secondary findings of Incident Response Trends in Q3 2022
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) was either not enabled for nearly 18% of engagements or it was only enabled for a small number of accounts and essential services.
Tools employed by adversaries were primarily focused on acquiring and gathering credentials, demonstrating the potential value of these tools in advancing an adversary’s goals.
Talos has been keeping an eye on the rise in the use of dual-use tools like Anonymous Fox, Brute Ratel, Sliver, and Manjusaka in these attacks.
Threats include phishing and business email compromise (BEC), attempts to exploit flaws or vulnerabilities in publicly accessible apps, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults, and insider threats were all still being observed by CTIR.

A variety of publicly accessible tools and scripts support adversarial goals.
To enable operations at various phases of the attack lifecycle and saw adversaries use a number of publicly accessible tools. And scripts that were either housed on GitHub repositories or were available for free download from third-party websites.
Password spraying is a method of obtaining credentials that involves trying a single password or a set of frequently used passwords against numerous accounts in an effort to verify credentials and gain access. The PowerShell script will cause a significant number of account lockouts, which correspond to customer-reported activities.
Talos keeping an eye on the rise in the use of dual-use weapons like Manjusaka, Cobalt Strike, Brute Ratel. Given that the toolkit was cracked in late September. The tool kit is now freely available on a number of hacking forums and communities, Brute Ratel is especially concerned.