The Checkmk IT Infrastructure monitoring software has vulnerabilities that have been publicly revealed and could be exploited by a remote, unauthenticated attacker to completely take control of the vulnerable systems.
Stefan Schiller, a SonarSource researcher, wrote in a technical study. These vulnerabilities can be chained together by an unauthenticated, remote attacker who can gain code execution on the server using Checkmk version 2.1.0p10 and lower.”
Also read, There are two fresh zero-days for Exchange Server
Based on Nagios Core, Checkmk’s open-source monitoring tool integrates with NagVis for development. And viewing topological maps of infrastructures, servers, ports, and processes.
By reviewing the Checkmk IT infrastructure monitoring software vulnerabilities. Over 2,000 clients utilize its Enterprise and Raw editions. They include Airbus, Adobe, NASA, Siemens, Vodafone, and the company tribe29 GmbH, based in Munich.
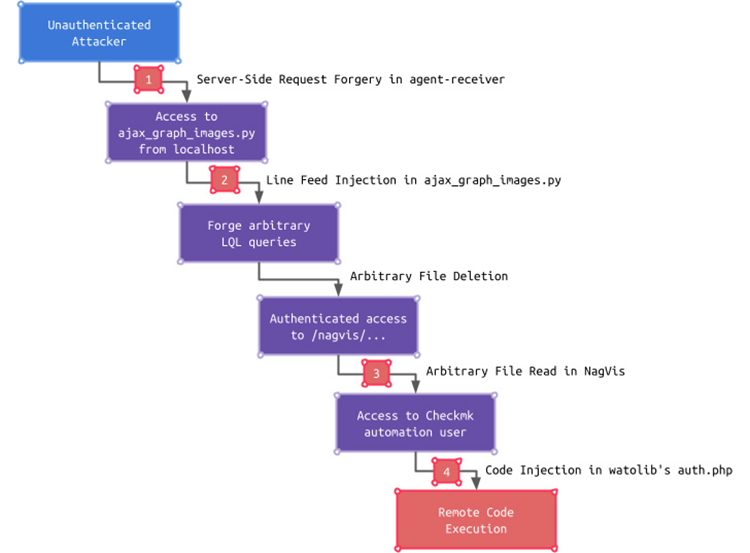
The Bugs in Checkmk
The four bugs, two of Critical severity and two of Medium severity, are as follows:
- Authentication vulnerability in Watolib’s auth.php CVSS rating: 9.1
- NagVis’s arbitrary file read vulnerability (CVSS score: 9.1)
- Unsafe command injection Python API and Checkmk’s Livestatus wrapper (CVSS score: 6.8), and
- The host registration API contains a server-side request forgery (SSRF) vulnerability (CVSS score: 5.0)
While each of these flaws by themselves has only a minor effect, they can all be exploited together by an adversary to gain access to the Checkmk GUI. They can start by using the SSRF flaw to access an endpoint that is only accessible from localhost, then use it to skip authentication and read a configuration file.
By taking advantage of a Code Injection vulnerability in the watolib Checkmk GUI subcomponent, which creates the auth.php file necessary for the NagVis integration, this access can be converted into remote code execution, according to Schiller.
Also read, Avos ransomware organization increases its attack capabilities
The four vulnerabilities have been addressed in Checkmk version 2.1.0p12, which was released on September 15, 2022. It follows their responsible disclosure on August 22, 2022.
The revelations come after a number of holes in other monitoring tools. They include Zabbix and Icinga, which were found at the beginning of the year. These flaws might have been used to compromise servers by executing arbitrary code.