FFDroider and Lightning Stealer are two different information-stealing malwares that are capable of syphoning data and initiating subsequent attacks, according to cybersecurity analysts.

In a paper published last week, Zscaler ThreatLabz researchers Avinash Kumar and Niraj Shivtarkar stated, “Designed to deliver stolen credentials and cookies to a Command & Control server, FFDroider disguises itself on victim’s workstations to look like the instant messaging application ‘Telegram.'”
As the name implies, information stealers are capable of harvesting sensitive data from compromised workstations, such as keystrokes, screenshots, files, saved passwords, and cookies from web browsers, which are subsequently sent to a remote attacker-controlled domain.
FFDroider is spread via cracked installations and shareware with the primary goal of obtaining cookies and credentials linked with popular social media and e-commerce sites, then using the stolen data to log into the accounts and steal other personal account-related information.
Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Edge are among the browsers attacked by the spyware.
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Amazon, eBay, and Etsy are among the websites targeted.
“Using stolen cookies, the thief logs into victims’ social media sites and harvests account information, such as Facebook Ads-manager to run malicious adverts with saved payment methods and Instagram via API to steal personal information,” according to the study.
FFDroider also has the ability to download new modules from an update server, allowing it to grow its feature set over time and allowing bad actors to utilise stolen data as a route for gaining early access to a target.
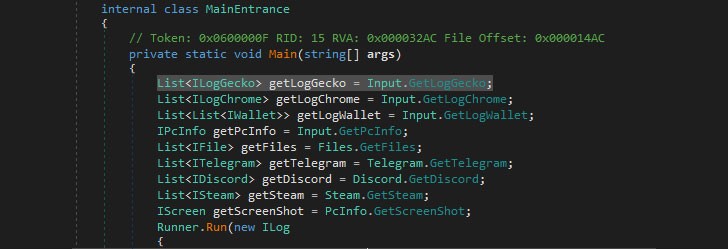
Lightning stealer works in a similar way, stealing Discord tokens, cryptocurrency wallet data, and cookies, passwords, credit card information, and search history from more than 30 Firefox and Chromium-based browsers, all of which is sent to a server in JSON format.
“We’ve seen ransomware groups leveraging Info Stealers to gain initial network access and, eventually, exfiltrating sensitive data,” Cyble researchers said, adding that “we’ve witnessed ransomware groups leveraging Info Stealers to gain initial network access and, eventually, exfiltrating sensitive data.”
The development comes as stealer malware has become more widespread in recent months across a variety of assault tactics, partly to fill the hole created by Raccoon Stealer’s withdrawal from the market in late March owing to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
Cyble Research revealed details of an upcoming threat named Jester Stealer in February 2022, which is designed to collect and transfer login credentials, cookies, credit card information, and data from password managers, chat messengers, email clients, crypto wallets, and gaming apps to attackers.
Since then, at least three different info-stealers have been discovered in the wild, including BlackGuard, Mars Stealer, and META, the latter of which has been seen being distributed via malspam operations to acquire sensitive data.
Source: https://thehackernews.com/2022/04/researchers-warn-of-ffdroider-and.html





