The Zscaler ThreatLabz research team discovered a PHP (malware) version of the ‘Ducktail’ Infostealer distributed as a cracked application installer for a variety of applications such as games, Microsoft Office applications, Telegram, and others.
Notably, Ducktail has been active since 2021, and experts believe it is run by a Vietnamese threat group. The primary goal of this attack campaign is to gain control of Facebook Business accounts.
Also read, Microsoft Office flaw identified by researchers
The Attack Chain
“Previous versions (as observed by WithSecure Labs) were based on a binary written in. To exfiltrate data, NetCore uses Telegram as its C2 channel.” Zscaler
The malicious installer in this case is hosted on a file hosting website. Researchers claim that changes have been made in the execution of malicious code when compared to previous campaigns. Furthermore, threat actors have switched to a scripting version in which the main stealer code is a PHP script rather than a. Binary on the internet.
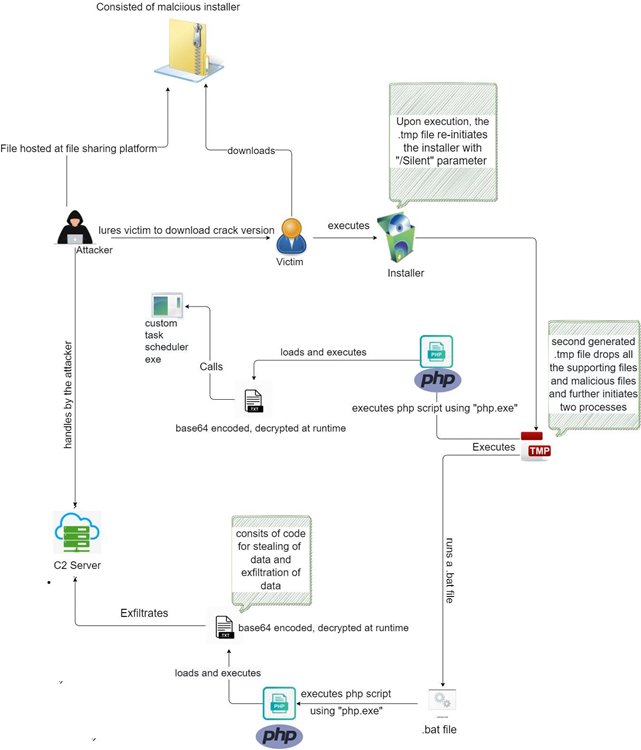
Attack Flow
“When run, the bogus installer displays a ‘Checking Application Compatibility’ GUI in the frontend.” “In the backend, it generates a.tmp file that re-initializes the installer with the “/Silent” parameter, and then another.tmp file is generated,” Zscaler researchers explain.
Also read, Phishing attacks using Microsoft 365 pose as US government agencies.
The PHP script contains decryption code for a base64 encoded text file. As a result of executing the decrypted version of the text file, the custom job scheduling binary will be executed.
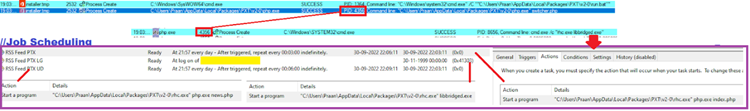
Job Planning
According to the researchers, the stealer code is decrypted in memory at runtime and then performs stealing and data exfiltration.
- Malware’s Functionality
- Retrieves browser information from the system.
- Retrieves browser cookie information from the system.
- Facebook Business accounts are targeted.
- Looks in the wallet.dat file for crypto account information.
- Data is collected and sent to the command and control (C&C) server.
Furthermore, the malicious script collects information about installed browsers in the system and extracts and copies critical data from them, such as machineID, browser version, and filename.
Stealing Information from Facebook Pages
In this instance, the malware examines various Facebook pages in order to steal information. These pages are associated with the Facebook API graph, the Facebook Ads Manager, and the Facebook Business accounts.
The malicious code will gain access to account and payment cycle details by searching for Facebook Business Ads Manager links. The malware attempts to obtain the following information from Facebook Business pages:
- Payment initiated
- Payment required
- Verification Status
- Owner ad accounts
- Amount spent
- Currency details
- Account status
- Ads Payment cycle
- Funding source
- Payment method [credit card, debit card etc.]
- Paypal Payment method [email address]
- Owned pages.
Following that, the PHP script attempts to connect to the C&C server in order to retrieve the list of contents stored in JSON format, which will be used to gather information.
“The ducktail stealer campaign is constantly changing or improving the delivery mechanisms in order to steal a wide variety of sensitive user and system information targeting users at large,” the researchers wrote.





